MPC vs AA: Rivals or Allies?

Table of Contents:
The wallet serves as the critical bridge to Web3.0, playing a pivotal role in achieving mass adoption for the crypto industry. Despite numerous efforts in improving wallet user experiences, the complexity of managing private keys and mnemonic phrases in self-custodial wallets, coupled with security concerns in custodial wallets, leaves users yearning for simpler authentication methods.
Enter the developer-focused MPC Wallet SDK and the recently deployed Account Abstraction (ERC-4337) Ethereum standard. These advancements provide a fresh perspective on Web3 development possibilities. However, as they gain traction, developers and enthusiasts alike often find themselves in complex technical discussions, uncertain of the ideal direction for the future.

In this post, we’ll explore how these seemingly conflicting concepts can actually complement each other, enhancing the ecosystem and benefiting users.
MPC Wallets:
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets leverage cryptographic algorithms, enabling multiple parties to jointly compute a signature while keeping their respective secrets private. This distributed key management approach offers improved security and resilience against attacks and accidental private key loss.
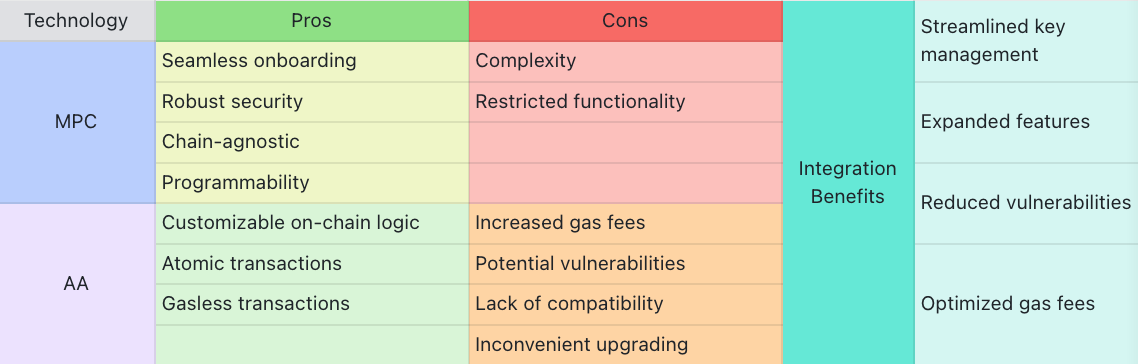
Pros:
- Seamless Onboarding: MPC wallets can facilitate user-friendly onboarding processes by integrating social logins, such as Email, Google, or Apple ID, simplifying the process for new users.
- Robust Security: Distributing private keys into several parts enhances the security of MPC wallets by eliminating single points of failure.
- Programmability: Since key shares can be hosted on servers, advanced features such as risk control and adaptable access management can be implemented.
- Chain-Agnostic: MPC wallets can operate across different blockchain networks, offering increased compatibility and versatility.
Cons:
- Complexity: MPC wallet implementation and management can be more complicated compared to traditional wallets.
- Restricted Functionality: MPC wallets primarily focus on key management, potentially lacking features found in smart contract wallets, such as gasless or pre-funded transactions.
Smart Contract Wallets (Account Abstraction or AA Wallets):
Smart Contract Wallets, especially those following the Account Abstraction (AA) standard, utilize smart contracts to manage user accounts. AA Wallets empower users with customizable, feature-rich interfaces, allowing them to define their own account logic and access features such as multi-sig, social recovery, and on-chain access controls.
Pros:
- Customizable On-Chain Logic: AA wallets centralize account-related configurations on-chain, enabling tailor-made wallets to meet specific user needs.
- Atomic Transactions: Users can combine multiple actions into a single transaction.
- Gasless Transactions: Decoupling signature signing and transaction submission enables users to delegate gas payments, which can be settled in various cryptocurrencies or even fully subsidized.
Cons:
- Increased Gas Fees: Smart contract wallet transactions may incur higher gas fees due to their complexity.
- Potential Vulnerabilities: Smart contract reliance exposes wallets to potential vulnerabilities or flaws in contract code.
- Compatibility Challenges: AA implementations may differ across chains or virtual machines, necessitating standardization and auditing efforts.
- Inconvenient Upgrading: On-chain smart contract wallet upgrades for new features or security enhancements can be expensive, especially on a large scale.
Synergy Between MPC Wallets and AA Wallets: The Best of Both Worlds
Integrating the strengths of both MPC and Smart Contract wallets mitigates the disadvantages of each technology:
- Streamlined Key Management: Incorporating MPC key management into smart contract wallets simplifies user experiences, enabling social account logins and seamless onboarding.
- Expanded Features: Combining MPC and smart contract wallets provides access to a full range of features, including atomic transactions, gasless transactions, and enhanced security.
- Reduced Vulnerabilities: Integrating MPC key management adds an extra layer of security against potential smart contract vulnerabilities and vice versa.
- Optimized Gas Fees: Integrating MPC can help reduce transaction costs through more efficient key management and fewer transactions related to key updates or recovery.
Although MPC and AA wallets are often portrayed as competing technologies, they can actually function as complementary solutions that enhance security, functionality, and user experience. By harnessing the strengths of both technologies, users can enjoy a more secure, flexible, and feature-rich wallet experience, paving the way for broader adoption and a more robust decentralized economy.
Particle Network, a full-stack Web3.0 development platform, has already implemented SDKs for developers to seamlessly integrate in-app MPC-based authentication and wallet solutions. Recognizing the importance of Account Abstraction in the Ethereum ecosystem, Particle Network is now actively developing a suite of tools to facilitate the creation of AA wallets that combine the advantages of MPC. Keep an eye out for upcoming innovations that will further elevate the world of Web3 wallet experiences.
Particle Network's Wallet Abstraction solutions are 100% free for developers and teams. By integrating them, you can set your project in a path to leveraging chain abstraction.
About Particle Network

Particle Network powers chain abstraction, addressing Web3's fragmentation of users and liquidity. This is enabled by Particle's Universal Accounts, which give users a unified account and balance across all chains.
Share this article
About the author(s)


